| CNAdbCC | |||||
CNAdbCC is a curated database for copy number aberrations analysis and visualization of cervical cancer. Currently, the database contains about 1,000 dataset samples mainly integrated by affymetrix and aligent platform. Affymetrix is based on light-controlled situ synthesis of DNA microarrays, and is the highest density and widely used chip preparation technology. In addition, agilent aCGH (array-based Comparative Genomic Hybridization) platform also provides high performance, high resolution chip data. The raw array data were collected from GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) and TCGA (The Cancer GenomeAtlas) databases. Genomic DNA copy number variations (CNVs), a type of structure variations, is one of the key hallmarks of carcinogenesis. |
|||||
| Data Processing & Database Contents | |||||
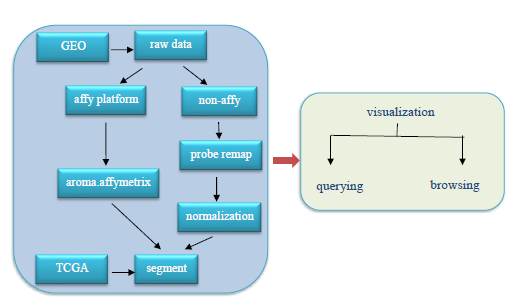
The raw data files are reanalyed to receive normalized data. The data processing pipeline is processed according to affymetrix and non-affymetrix platform respectively. For affymetrix platform, mainly processing use the R package—aroma.affymetrix. While, for non-affymetrix platforms, the process mainly includes calculated mean single probe, probe single remaping, base position normalization, delete ambiguous probes and so on. All the data were converted into segmentation data format and stored in CNAdbCC database. Users can view CNVs intuitively with user-friendly interface. |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
The pipeline for array data processing. |
Array data integrated in CNAdbCC. |
||||
| CNVs Frequency Profile | |||||
| The DNA copy number alterations profiling based on 974 samples is shown below. Overall, most frequent copy number aberrations were amplified of chromosome arms 3q (34%), 1q (22%), followed by 5p (20%) and 20q (17%). And losses of chromosome arms 4p (19%), 11q (18%), followed by 3p (15%) and 19p (13%). In particular, chromosomes 3q28 and 3q29 are the greatest alter regions in the entire genome amplification or deletion regions. |  |
||||
Genome-wide frequency plot of SCNAs. Copy number losses and copy number gains are in red and blue, respectively. |
|||||
| cervical cancer copy number variation database © 2019 Cai Laboratory | |||||