ESCC
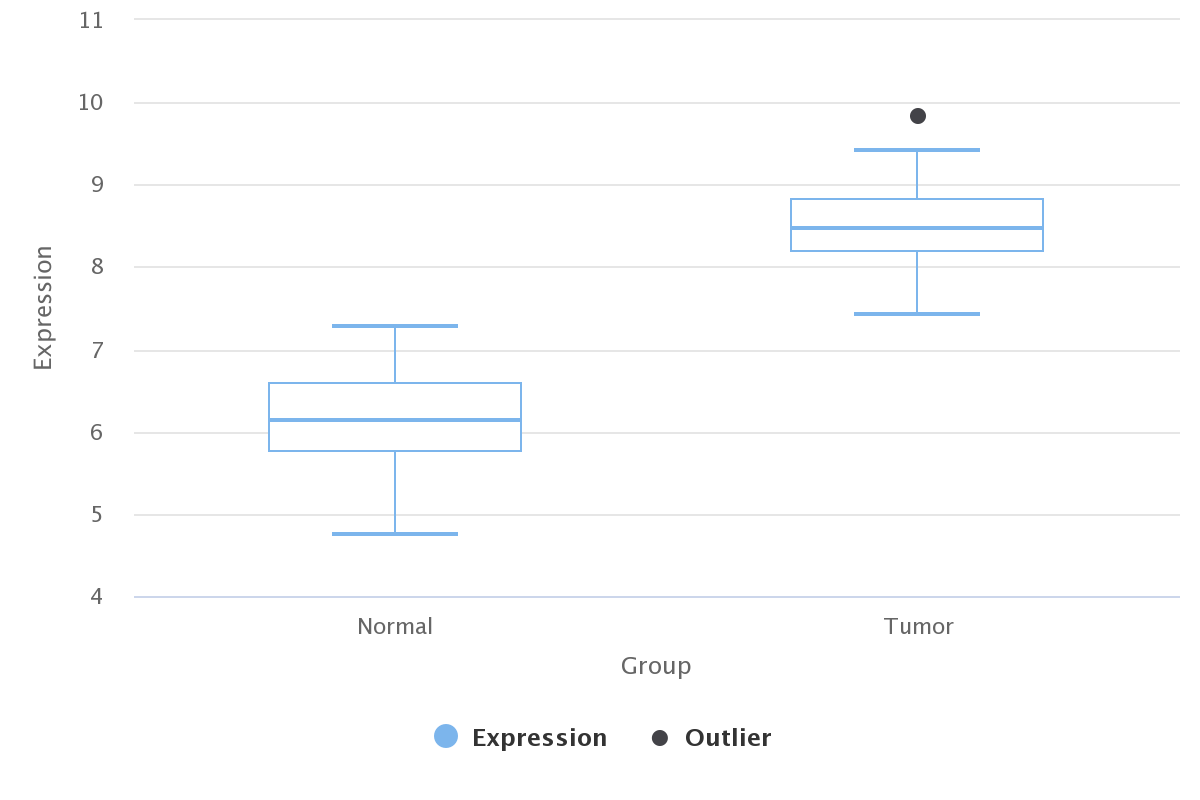
There are two major histological subtypes, Esophageal Adenocarcinoma(EA) and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC), respectively. The incidence of esophageal carcinoma ranks seventh (572,000 new diagnosis) while its mortality ranks sixth (509,000 deaths) (GLOBOCAN 2018, Freddie Bray, et al. CA Cancer J Clin.). The five-year survival rate is just 15%~25%. The high mortality highlights the necessity of detecting stable biomarkers, new druggable targets and investigating the molecular mechanism.
To facilitate the researches of ESCC, here we collected and uniformly processed gene expression, copy number and gene mutation data from GEO and TCGA database. We also provide an analyzing platform mainly based on gene coexpression to explore and identify potential candidates related to ESCC development.
Data collecting and processing
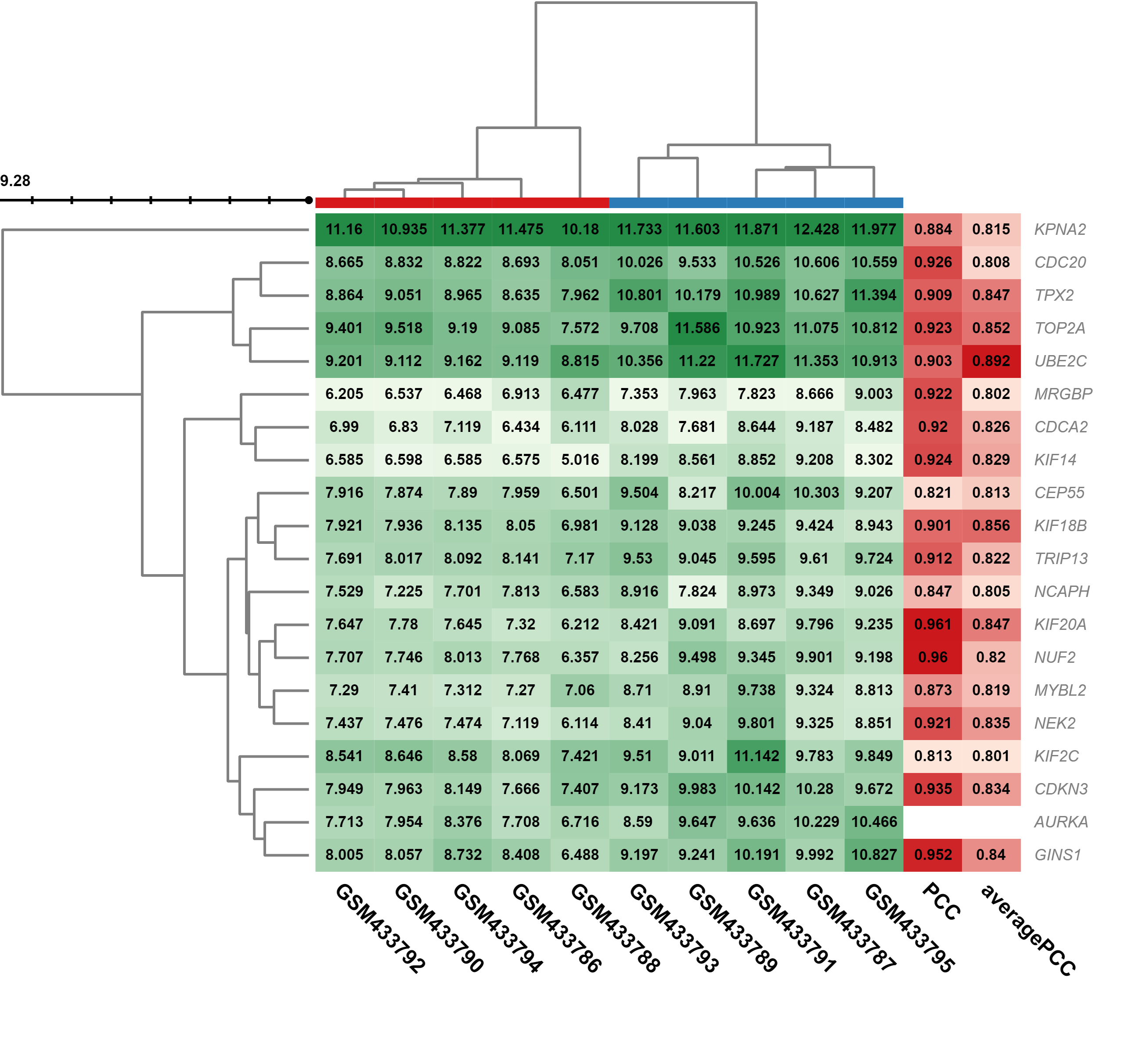
Gene expression chips were downloaded from GEO database. Quality control were applied to exclude low quality samples. Then each dataset was uniformly processed with background correction, within- and between-array normaliztion, probe filtration and differential expression analysis by limma R package. Gene coexpression analysis was based on normalized gene-level signals using Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC).
Copy number chips including genome-wide SNP arrays and comparative genomic hybridization arrays were downloaded from GEO database. Aroma.affymetrix or snapCGH R packages were used to do background correction, normalization and segmentation. Gene-level log2ratios were stored in database.
Gene mutations were collected from the supplementary materials of several publications. Mutations were uniformly annotated by annovar. Transcript-level annotations were mapped to proteins from uniprot and roteins' features and motifs were extracted from uniprot database.
Gene information were mainly collected from HGNC database. Gene involved pathways were extracted from Hipathia R package.
Analysis and presentations
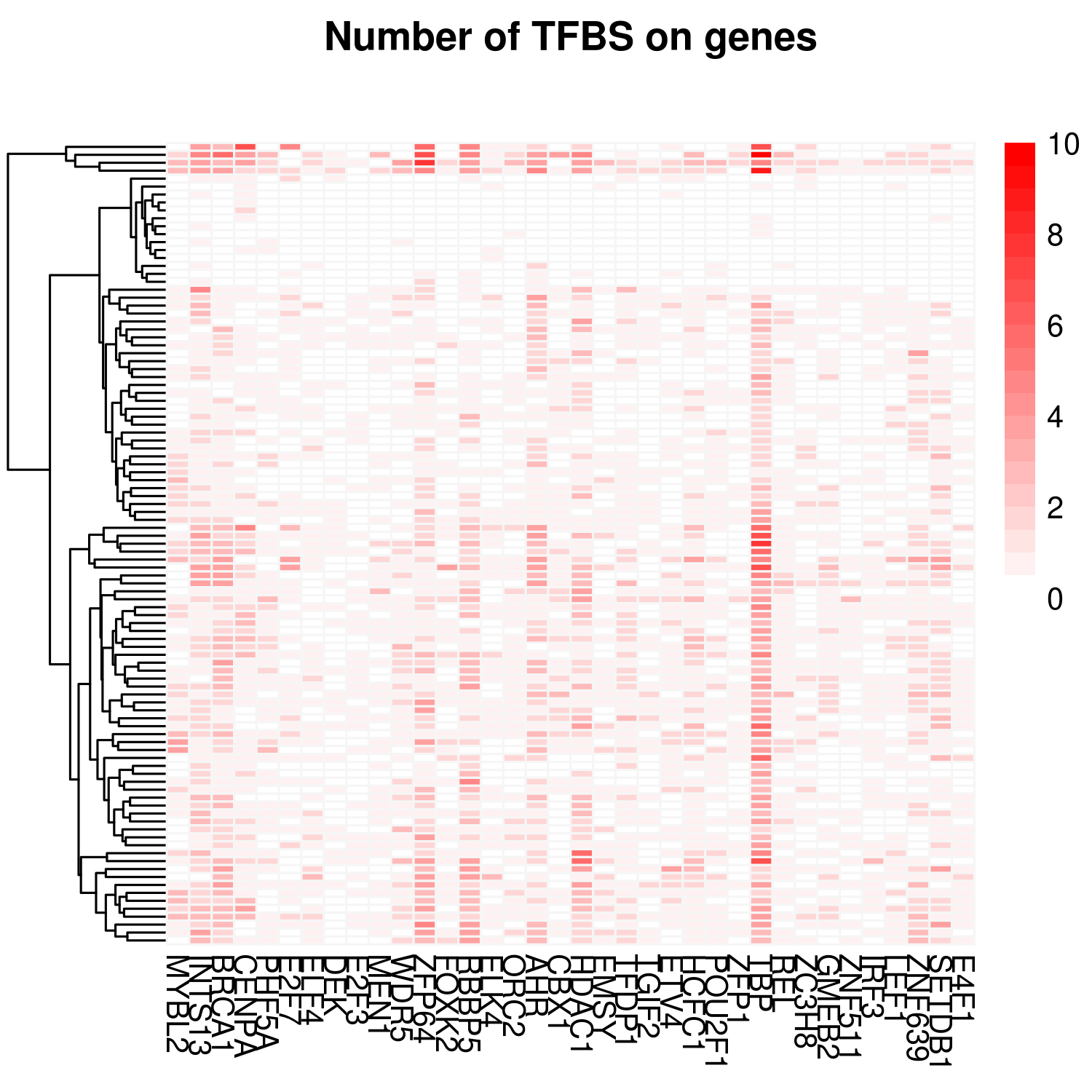
Gene coexpression and enrichment analysis can be carried out based on PCCs from a panel of gene expression chips. For each gene, we provide a list of highly correlated genes. These genes can be filtered by heatmaps in each dataset and further explored by transcription factor binding site enrichment.
Survival analysis is provided based on three datasets with survival information for each gene.